This is great insight from Cursor on long-running agents.
It turns out planning is all you need.
On a serious note, planning is critical to be productive and effective with AI Agents.
It's aligned with how I get Claude Code to effectively work on long-running tasks. (More of my thoughts on Claude Code towards the end of the post)
First, let's discuss the insights from the Cursor article.
The big problem with multi-agent systems today is the coordination/communication.
The solution Cursor proposes is careful planning.
I agree that the best way to deal with this challenge today is to do careful planning.
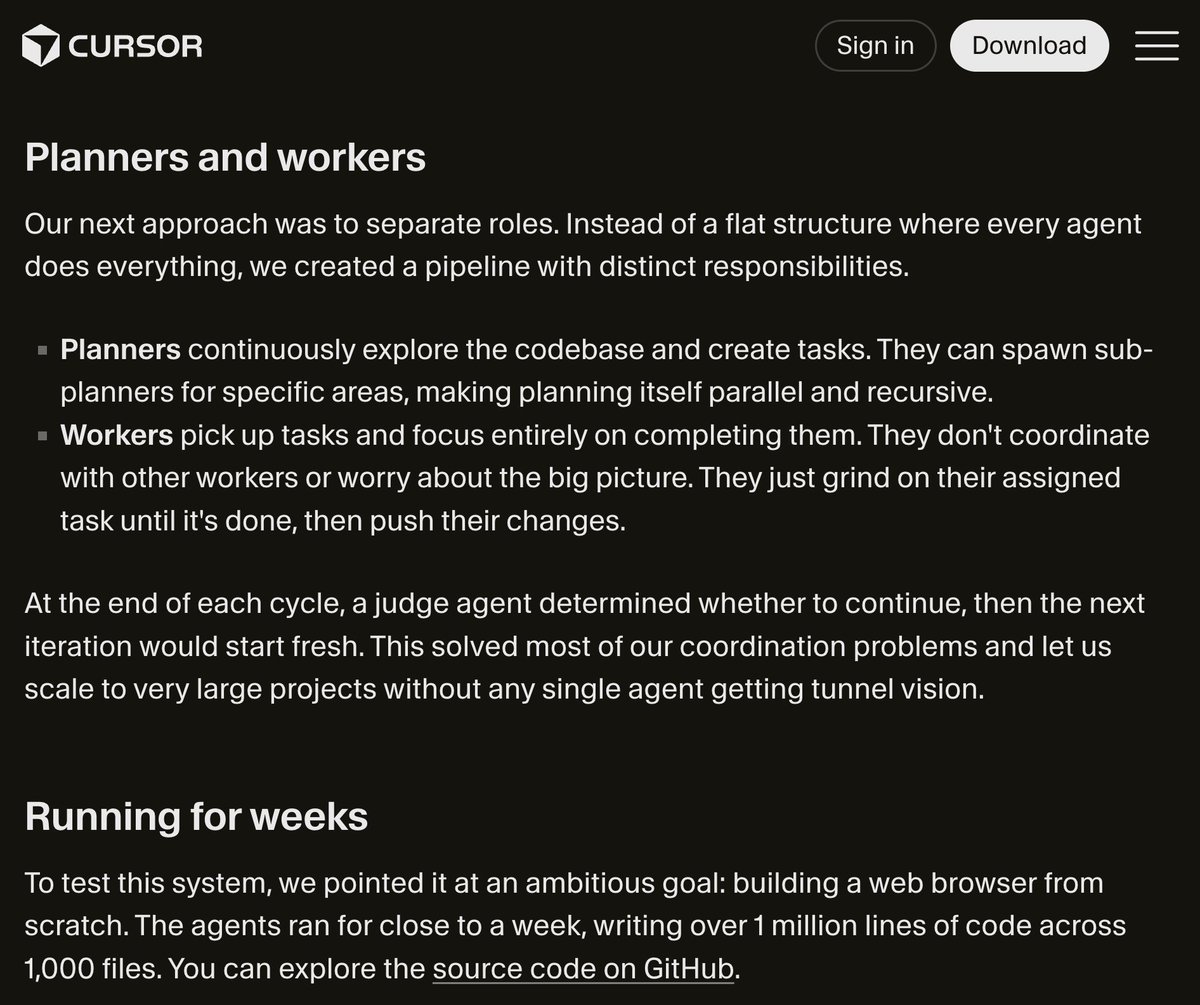
Planners can explore the codebase and create these tasks.
Then, subplanners are spawned to address specific categories of tasks. The great thing about this is that it enables parallelization and recursive loops, ideal for this kind of work.
From here, subagents can focus on assigned subtasks once they are completed (and push changes). One important aspect of this work is that subagents don't coordinate at all and are oblivious to the bigger picture. But they don't need to be to produce high-quality code that doesn't conflict. The issue with having subagents talk to each other is that this can lead to communication bottlenecks, duplicate work, and potential drift.
This can operate in cycles, which are all verified using a judge agent. The judge agent determines if work can continue or if there is an issue to address on every cycle.
Cursor managed to build a web browser from scratch with this approach. The agent ran for a week, writing over 1M+ lines of code across 1K files.
Cursor found that GPT-5.2 is better for this set up. They find that Opus 4.5 tends to stop earlier, take shortcuts, and quickly yield back control.
The simpler system worked best. "Too little structure and agents conflict, duplicate work, and drift. Too much structure creates fragility."
An interesting finding: designing an effective system prompt to focus over long periods was more important than the harness and models themselves.
Why this resonated with me, even though I am not a Cursor user:
I have been testing Claude Code on long-running tasks. And what Cursor reports is aligned with my own findings. However, better planning and tuning of the system prompt, including tuning CLAUDE MD, has allowed me to leverage Claude Code more effectively for these long-running tasks.
Here are a few notes on planning and how you get something like this to work in Claude Code:
You can do effective planning in many different ways. You can create an initial plan and complete it with Claude Code (in plan mode). Or you can brainstorm the plan with Claude Code directly (in plan mode). Claude Code is excellent at managing plans for you in case you don't want lots of moving parts. This, together with subagents works extremely well in Claude Code already. However, you can also get more creative with how planning is done to mimic the subplanners proposed by Cursor. Claude Code is extremely flexible with all its functionalities (Skills, Slash Commands, Subagents, Hooks, etc.). I will share more on this later after I finish with some experiments I am currently working on.
When planning, it helps if you are also involved in the process. If you are a Cluade Code user, you can trigger the AskUserQuestion tool to inject inputs that will help with making the plan robust.
From here, you can offload individual work to subagents (in parallel if you want). The great part about this is that in Claude Code subagents manage their own context, which keeps the main orchestrator's context clean and only for the high-level stuff. You can customize your subagents with models and tools. The planning is core for the coordination to work. The system prompt helps to maintain stability and better manage context. The subagents are just in charge of executing the work.
I will be sharing more on my setup in the coming weeks. I am fascinated by how far we can push agent harnesses for long-horizon tasks. Stay tuned!